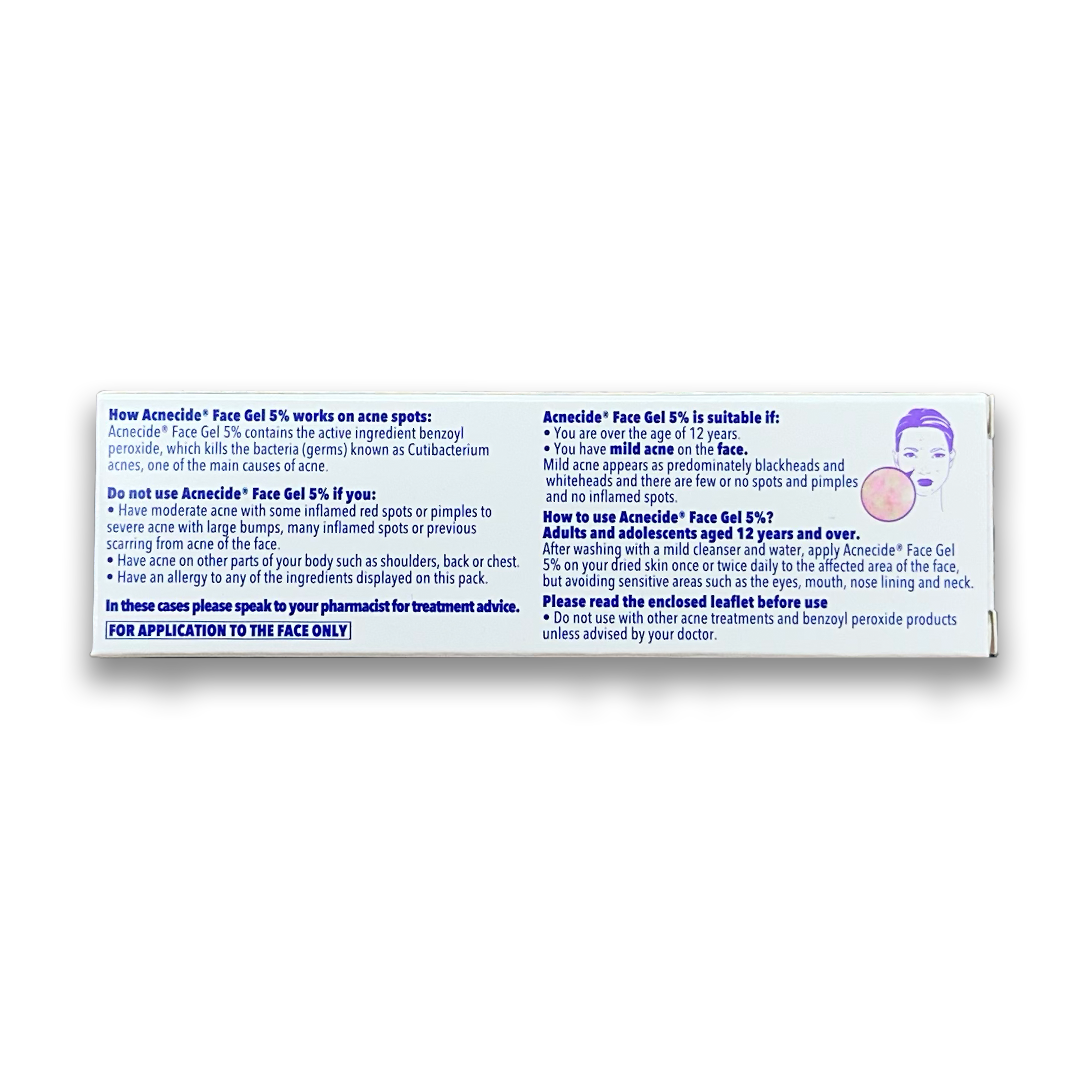
About Acne
Cause
Diagnosis
Treatments
Prevention
Further Info
FAQs
Can my diet influence the development of acne, and are there specific foods to avoid to prevent breakouts?
Is it safe to use over-the-counter acne products without a prescription, and what should I look for in these products?
Does sunscreen play a role in preventing or exacerbating acne, and what should I consider when choosing a sunscreen for acne-prone skin?
Are there specific skincare routines or products that can help prevent acne, even if I don't currently have acne?
We are here to help 👋
For assistance, please contact our customer service at info@rightangled.com. We are available Monday to Friday from 8 am to 5 pm. For urgent issues, please do not use this email. Instead, call 111, or dial 999 in case of an emergency.