Canesflor Probiotics Supplement
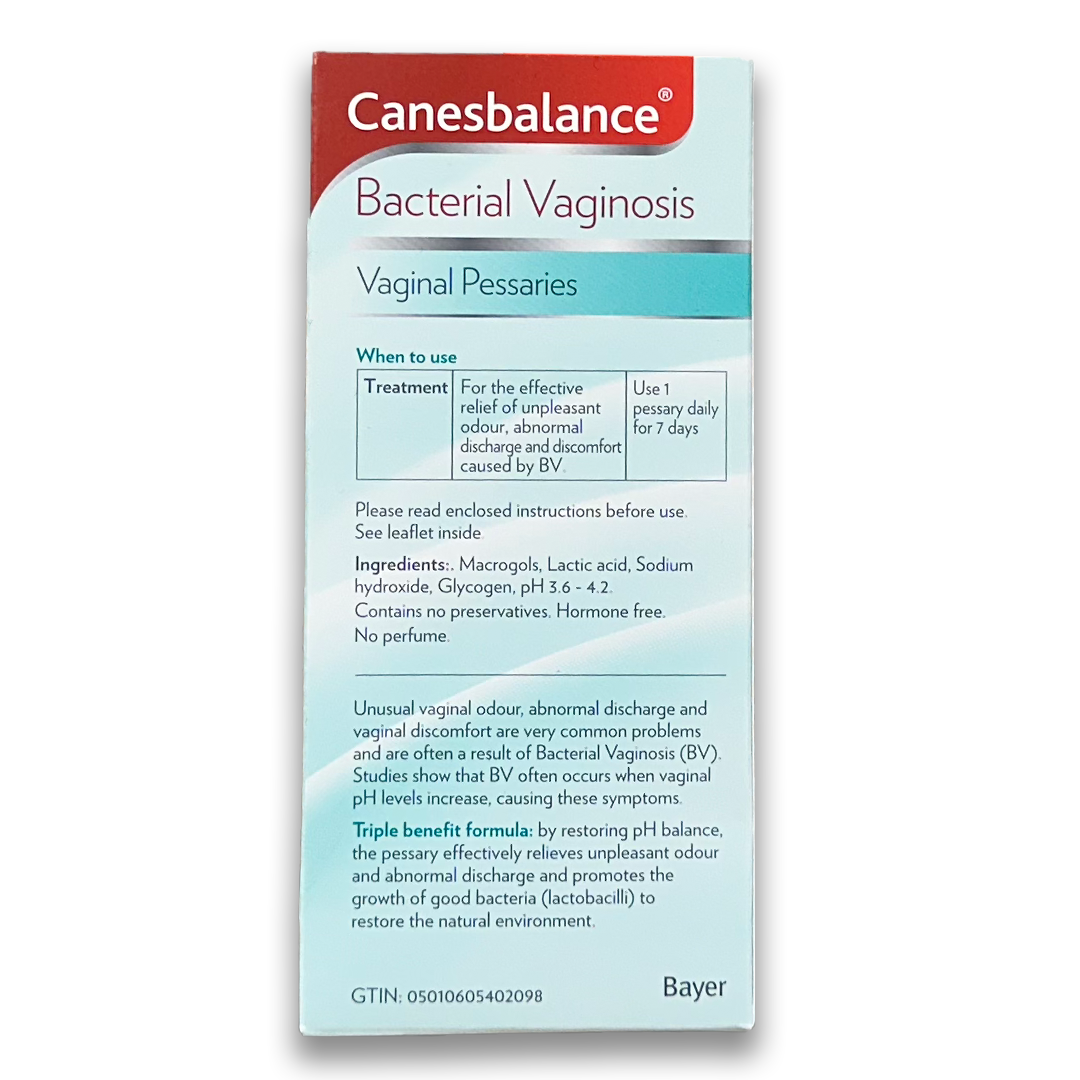
Canesbalance Bacterial Vaginosis


About Vaginal Thrush
Causes
Diagnosis
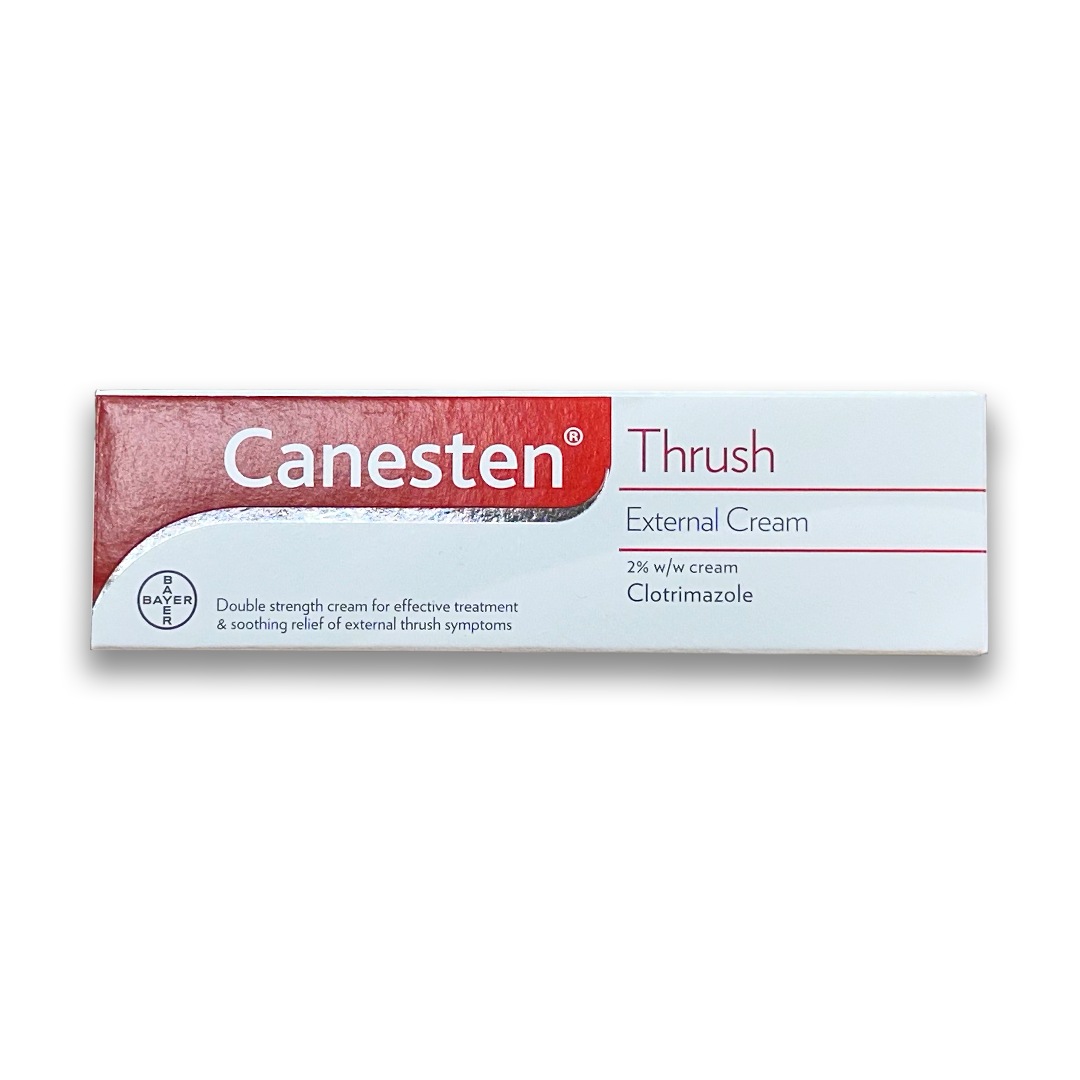
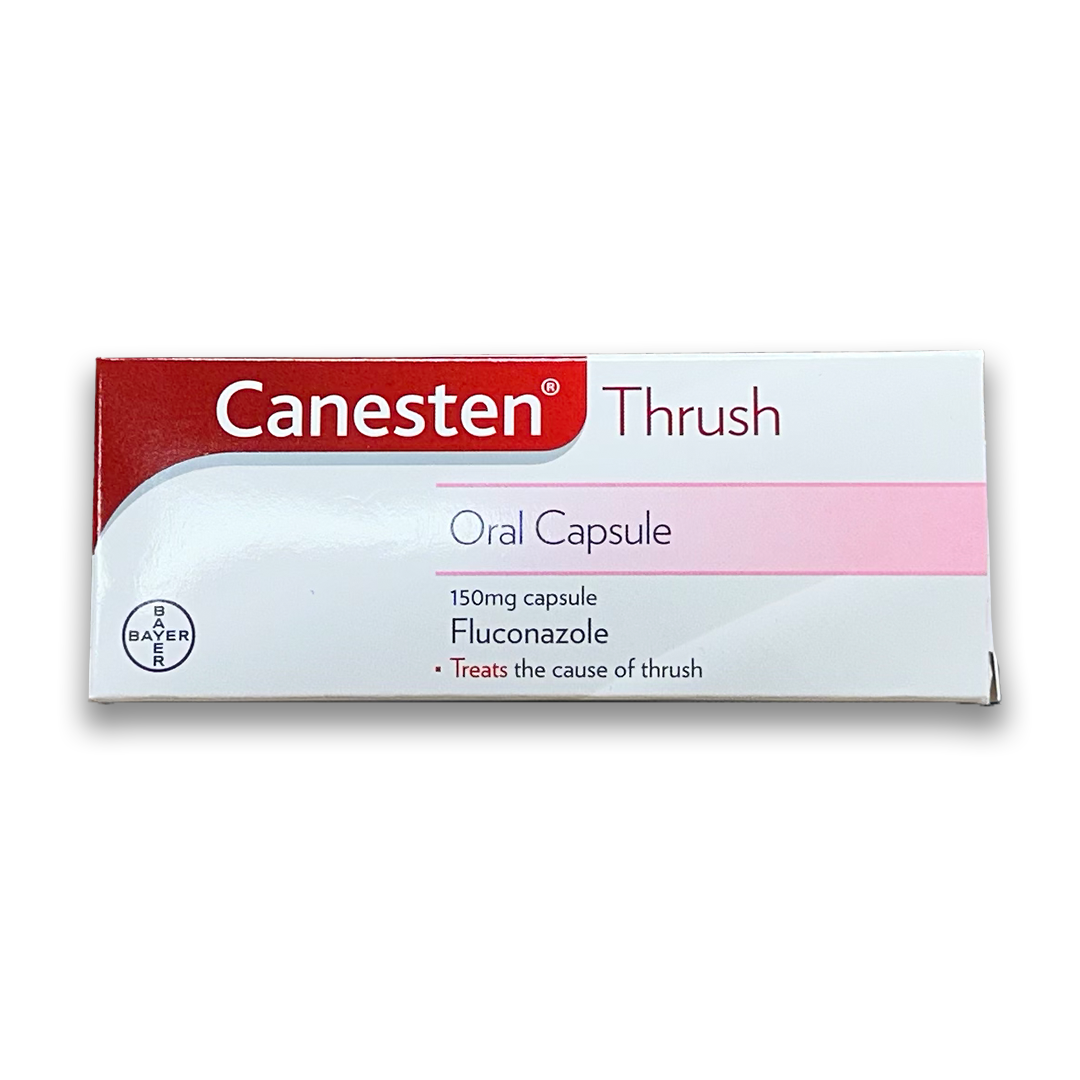
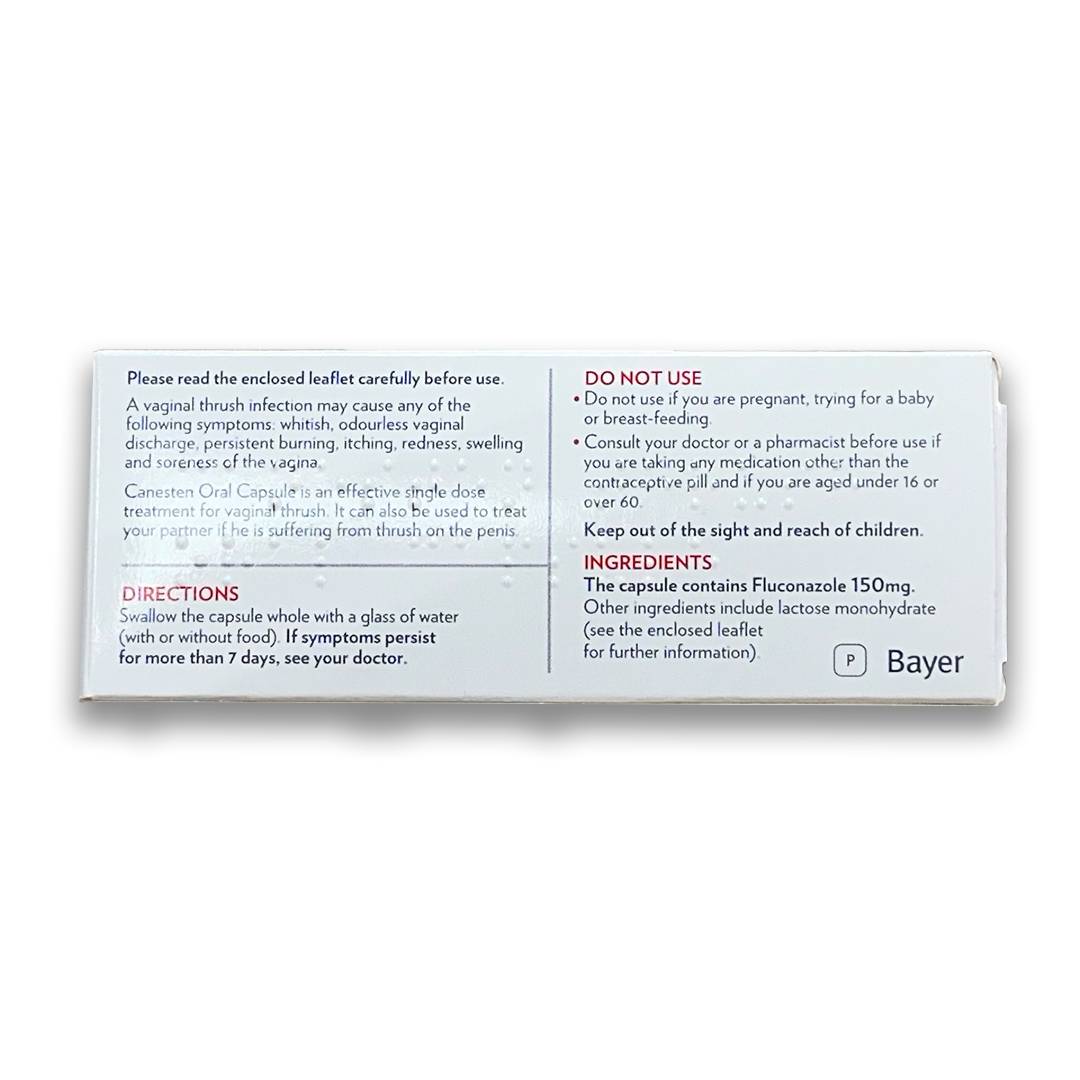
Treatments
Prevention
Further info
FAQs
Can men get thrush?
Can thrush be transmitted through sexual contact?
Are there risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing thrush?
Can I treat thrush with over-the-counter medications?
We are here to help 👋
For assistance, please contact our customer service at info@rightangled.com. We are available Monday to Friday from 8 am to 5 pm. For urgent issues, please do not use this email. Instead, call 111, or dial 999 in case of an emergency.